This tutorial is focused on a web based distributed application. If you are looking to build a mobile or desktop application then this tutorial is not for you.
Blockchain is the next step towards creating a more independent, peer-to-peer and decentralized system that could take the tech world by the storm. The tech world has been buzzing with words such as, ‘bitcoin’, ‘blockchain’ and ‘cryptocurrency’. Blockchain was originally created to support the Bitcoin but soon the tech community has started using this technology for other purposes.
Don & Alex Tapscott, author of Blockchain Revolution (2016) stated, “The blockchain is an incorruptible digital ledger of economic transactions that can be programmed to record not just financial transactions but virtually everything of value.”
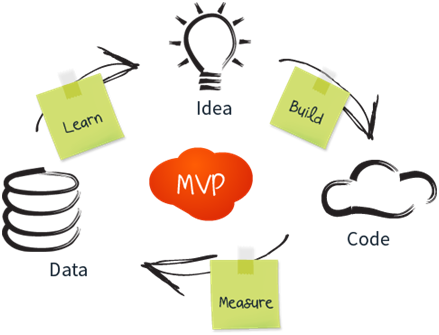
What is MVP?
A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is the most basic version of a product that can still be released. It constitutes of three characteristics:
- Is it valuable enough for people to buy it in the initial stages?
- Does it hold any future benefits for people who invest in the product initially?
- Does it hold any promise for future development or does it provide substantial feedback that dawns a new product?
https://www.techopedia.com/definition/27809/minimum-viable-product-mvp
Eight Steps to Build MVP
Step 1: Identify the MVP Requirements
It is very important to identify the MVP requirements. The initial step is to recognize the product’s core offering. You will need to take into consideration the features of the app and build them well. The second step is to take into consideration the audiences that you are catering the services to. You cannot include features in your app to please all kinds of audience. Hence, you should focus on the early adopters of your product. This will ensure that you get the feedback for your app. If your app replicates your competitor’s app then you need to build better features.
Step 2: Identify frontend frameworks for web based application (such as React.js, Angular)
Here, let’s identify how to build modern web applications and understanding the type of technology that you must choose.
React.js framework was created for Facebook; it introduced the idea of treating components like pure function and component parameters as function arguments. This framework provides a thin view layer, for example, it provides one piece of the puzzle and expects the developer to connect the rest of the pieces. This platform is best handled by experienced JavaScript developers who can deal with functional programming and immutable data structures. Your app will need to target several platforms with the same codebase. The React.js platform will allow you to write for the web, for native with React Native, and for VR devices with ReactVR.
Another platform, Angular.js introduces the idea of compiling templates to make it HTML dynamic. By using directives, you could bind a model to a view, and the same would change when the model changed. Angular.js is built by Google; this platform is perfect for enterprise developers who are coming from Java or C# background. The developers feel comfortable using this program as it supports TypeScript and Intellisense. The platform is used to build performance oriented native applications using NativeScript.
Step 3: Create front end wireframes and design application
There are 6 quick steps that can be followed to create front end wireframes and design application.
i.User research, requirement analysis, and inspiration
It is important to analyze the requirements, your user base and other competitive applications that have similar features. Once you determine the same, you can then proceed to create a wireframe.
ii.Choose the correct tools
There are many tools available in the market to create wireframes such as Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, Axure, GoMockingbird, Mock Flow, etc. Choose the one you are most comfortable with.
iii.Setting a wireframe layout or grid
Taking into consideration the device and technology, you can proceed to create the wireframe. For instance, depending upon your requirement create a desktop screen shaped layout and a 12 column or 9 column grid to create a website.
iv.Create feature layouts
The features of an application such as menus, input boxes and buttons are made in a specifi shape. With the help of wireframing tools, you can also create custom shapes in your grid, i.e. you can clearly distinguish individual design features.
v.Content and typography
Once the feature layouts are frozen, it’s time to update the boxes with necessary content. Choose the font and style that makes it unique.
vi.Polish the wireframe
You can further enhance the wireframe by adding logo and basic design elements. You can also add grayscale, shadings or colors to highlight images. Remember, presentation is key!
Step 4: Identify the data structures
Data structures are an intentional arrangement of a collection of data that is built to impose or enforce some kind of systematic organization on the data. Since all the information is from one place, it makes our lives easier. There are generally five fundamental behaviors that you perform with data; accessing data, inserting data, deleting data, finding data and sorting data.
Each data structure has its own algorithm for performing a behavior due to the nature of the data structure. The more efficient and suitable the algorithm, the more you will have an optimized data structure. These algorithms might be built-in or implemented by developer to manage and run these data structures.
It includes a clean and easy to operate interface, logical access, data flow and data transformations. It is important to note that every blockchain has its own strength.
For instance, fat blockchains can use a network to deploy and run programs or smart contracts. On the other hand, thin blockchains can only transfer assets from one account to the other because they have a set number of operations.
Similarly, public blockchains are open for all the users. They can join, transact and audit. A common example of a public blockchain is the Ethereum network that is used by Initial Coin Offering (ICO) campaigns to deploy and distribute smart contracts. On the other hand, private blockchains cannot be accessed by any participant. They need to be approved and on-boarded before hand by a federation.
Step 5: Write solidity contracts
Solidity is “a contract-oriented programming language for writing smart contracts. It is used for implementing smart contracts on various blockchain platforms”. It was developed by Gavin Wood, Christian Reitwiessner, Alex Beregszaszi, Liana Husikyan, Yoichi Hirai and several former Ethereum core contributors to enable writing smart contracts on blockchain platforms such as Ethereum. Solidity is a statically-typed programming language designed for developing smart contracts that run on the EVM. Solidity is compiled to bytecode that is executable on the EVM. With Solidity, developers can write applications that implement self-enforcing business logic embodied in smart contracts, leaving a non-repudiable and authoritative record of transactions.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solidity
As specified by Wood, “it is designed around the ECMAScript syntax to make it familiar for existing web developers; unlike ECMAScript it has static typing and variadic return types. Compared to other EVM-targeting languages of the time such as Serpent and Mutan, Solidity contained a number of important differences. Complex member variables for contracts including arbitrarily hierarchical mappings and structures were supported.”
http://gavwood.com/
Step 6: Front end development
You can develop your front end user interface and to interact with the data structures in the solidity contract by using the web3.js api.
web3.js is a collection of libraries which allow you to interact with a local or remote ethereum node, using a HTTP or IPC connection.
https://web3js.readthedocs.io/en/1.0/
The following points will help you through installing and running web3.js, as well as providing an API reference documentation with examples:
- To ensure that your app works on Ethereum, use the web3 object provided by the web3.js library. Under the hood it communicates to a local node through RPC calls. web3.js works with any Ethereum node, which exposes an RPC layer.
- web3 contains the eth object – web3.eth (for specifically Ethereum blockchain interactions) and the shh object – web3.shh (for Whisper interaction).
Step 7: Deploy on test network and perform testing
Test network includes lightweight testnet and heavyweight testnet. Heavyweight testnet is used for large scale networked testnets. For example, Geth is useful for connecting to public networked testnets such as Ropsten. Ropsten is essentially the Ethereum network with free ETH and poor security.
Ropsten is required only when you are getting into the advanced stages of development. An easier way to connect to Ropsten, is by using MetaMask. “This browser extension provides easy access to Ropsten using the INFURA public Ethereum nodes. This means you do not have to run your local Geth node. MetaMask injects a web3 object into your frontend which is preconfigured to use the public Ropsten network.”
https://karl.tech/intro-guide-to-ethereum-testnets/
Step 8: Deploy on main net
Deploy the application on main network and announce to the world.
This includes understanding the benefits that the business offers and barriers that one might face while launching the app or after launching the app. McKinsey estimates that B2B payments yield the biggest cross-border revenues for banks, with such transactions representing 75% of all cross-border payments that total to more than $150 trillion in 2015.
Cross-border payments are inept because there is no one single way of global payment system. Five challenges must be overcome to improve the cross-border process:
Infrastructure: Most payment systems are based on local laws and practices within existing domestic banking and financial structures. Hence, domestic infrastructures are not designed to handle cross-border payments.
Standards: The bank and corporate treasury/enterprise systems cannot pass data to each other has there are no common global standards or variations set.
Regulations: Government regulations are changing how payments are made. Due to the varying roles between the originating and receiving country, payments are subject to domestic regulations.
Speed: According to McKinsey research on cross-border payments, the average time to complete a cross-border transaction is three to five business days.
Opacity: It’s usually difficult for senders and receivers to track their payments while the funds are in transit, which makes the delivering time and receiving the final payment a little more cumbersome. Tracing incorrect account numbers can be really difficult in case of an error in transaction.
Conclusion
Blockchain can become a unified protocol that companies would use to write and read data. Transparency can be improved through a shared ledger, the speed of transactions can be increased, and standards can be improved with the help of a distributed ledger technology.
Hence, to understand this in its entirety, start small. Choose a point problem and do MVPs. Since, blockchain technologies are constantly changing, make sure that you can build an app that can build production-grade solutions on top of those MVPs.
App-Scoop blockchain developers can help you create your blockchain MVP for your business.
Contact app-scoop team – https://app-scoop.com/contact-us.html