Over the past few years, there has been a significant amount of development in the
Internet of Things (IoT), which is essentially a group of interconnected devices functioning together. While there has been a lot of growth in the consumer facing side, which is IoT, there has also been a significant amount of growth in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), which is more manufacturing focused.
IIoT had a worldwide value of $295 million in 2015, an this expected to grow to a value of $1.6 billion by 2021 with a CAGR of 33%. Furthermore, IIoT is expected to have an economic impact of approximately $6 trillion by 2025, out of which $1.3 trillion will be for the electricity industry1.
While there is a large potential for this technology, it will take time for IIoT to be a standard as there are high costs to implement the system and make older manufacturing models compatible with IIoT.
What is IIoT
The Industrial Internet of Things is similar to the Internet of Things, in the sense that multiple devices and sensors work together on the same network to collect and analyze data. The main difference is that IIoT uses these sensors to collect large amounts of data and analyze it to improve and even automate current processes, making the manufacturing experience more efficient. IIoT is already growing in demand as large companies are in the process of rolling out IIoT solutions such as IBM’s Watson. GE’s Predix, and Honeywell’s Sentience.
Current Demand for IIoT

A survey by PwC revealed the current interest for IIoT and digital factories. Approximately 90% of respondents and investing in digital factories, but only 6% consider their manufacturing processes to be completely digitized. Almost majority of respondents chose to invest in digital factories to better server customer preferences and improve the manufacturing process efficiency. The expected ROI for an investment in a digital factory is at around 50%, making it an attractive investment. Furthermore, companies are expected to see an improvement in efficiency by more than 10% over the next five years as they roll out IIoT implementations in their factories.
Almost 50% of respondents expect IIoT to increase employee productivity, improve asset optimization, and reduce costs However, some potential barriers include poor communication of infrastructure requirements and high capital costs. Furthermore, 40% of companies said lack of government support makes it more difficult to implement IIoT in their factories and around 20% said there is insufficient technical knowledge in the workforce to truly benefit from IIoT being implemented.
Trends in IIoT

Data Analytics
There are multiple companies that are brining data analytics to manufacturing. Companies are expecting to invest in digital literacy rather than infrastructure as IIoT becomes more popular1. There is no more of a focus on how to collect data and use it in a valuable way to improve processes. This is where IIoT plays a large role, as multiple sensors can ready key inputs from multiple machines and analyze this data to make meaningful conclusions about how a factory process is running. Factories are now looking at hiring non-traditional roles such as data scientists and engineers to leverage this data to make smart predictions. Companies such as Microsoft, Amazon, and Google are already looking into how to allow such analytics to be used at scale with low costs.

Application Development
While there will be a large focus on using the data, there will also be increase in application development that will use this data to provide a user experience where factory managers can read the data in meaningful ways such as visual reports. Factory asset management can also be done through these apps as sensors can provide key points of data such as what level of efficiency a machine is running at, when the last maintenance was done, and real time location of machines and vehicles on the factory floor1. The application can also have functionality for factory managers to perform actions remotely such as powering machines, requesting maintenance, and other functions.

Energy Harvesting
As costs of fuels increase, companies are looking into more energy efficient technology that are cheaper such as solar, thermal, and wind energy. Capturing this energy efficiently and monitoring how much energy is captured so that it can efficiency be distributed based on factors like the current workload. A machine that currently requires larger amounts of electricity as it is performing a heavier task can have power rerouted from idle machines that do not need it at the moment. This will help energy be utilized better, reducing wastage and costs.
Predictive Maintenance
The factory machine maintenance industry has nearly 20 million field technicians that maintain a variety of difference machinery1. Maintaining these machines is extremely expensive, and not efficient now. Machines that need maintenance are being used without factories aware, which leads to more expensive breakdowns and down time. On the other hand, machines that are functioning better than expected are receiving maintenance. Through the use of IIoT sensors, data can be collected on machine usage and uploaded to the cloud. This data can be analyzed to determine what input factors, like machine hours used, type of equipment worked on, or others impact a machine the most by plotting this data to find correlations using regression. Furthermore, based on usage, a general point of maintenance can be determined that is significantly more accurate than time-based maintenance. For instance, a machine can be maintained once every 10,000 hours of usage versus once every year1. This allows factors that actually impact the machine to be used to determine when a machine is maintained, allowing machines that need the maintenance to be repaired first.
Security
Like in IoT, security will be a key factor in IIoT as well. Devices will now have longer usage cycles, and its important to keep the software up to date and secure throughout this entire process. Nearly 96% of security professionals in organizations are expecting an increase in cyber-attacks on IIoT infrastructure3. Many factories currently do not feel prepared for such attacks as they can cripple an entire factories ability to produce items. It is extremely important to take the appropriate security measures to ensure data is transmitted securely and machines have the proper authentication in place.
Automation
As IIoT becomes more popular, there will be an increase in autonomous capabilities. As more data gets collected, machines can start to make key decisions autonomously, such as when to request a repair if a particular part is not running efficiently1. Furthermore, through the use of more sensors, the manufacturing process can have more machines involved to streamline production.

Data Centers
While not limited to just IIoT, Data Centers will transform to become more autonomous. IoT and AI will enable data centers to self diagnose issues to find their root cause and diagnose the problem immediately. There will also be preventive measures taken if a data center predicts an issue will arise. This is extremely important as data is at the heart of IIoT, and if a data center is down, it will have a large impact on operations. There will also be reduced costs as data center administrators will not be needed as often to fix these issues. Further technologies will allow data center administrators to manage data servers remotely and monitor status and progresses, allowing an administrator to work on an issue upon a company’s request regardless of where they are.

Leveraging AR and VR
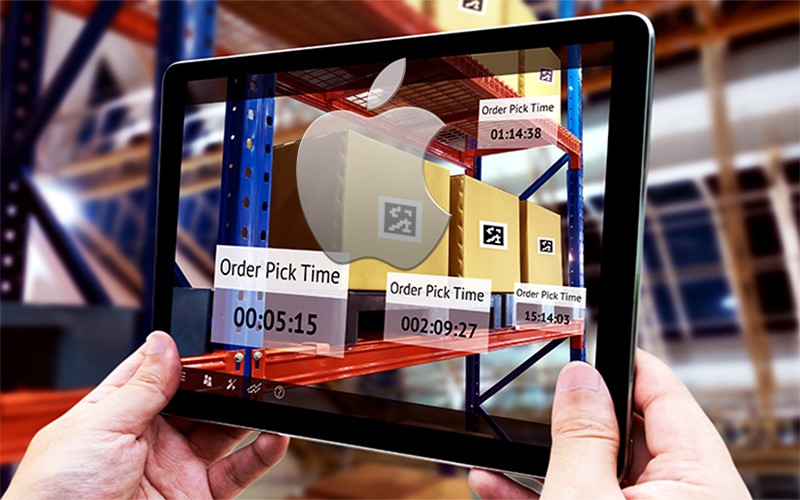
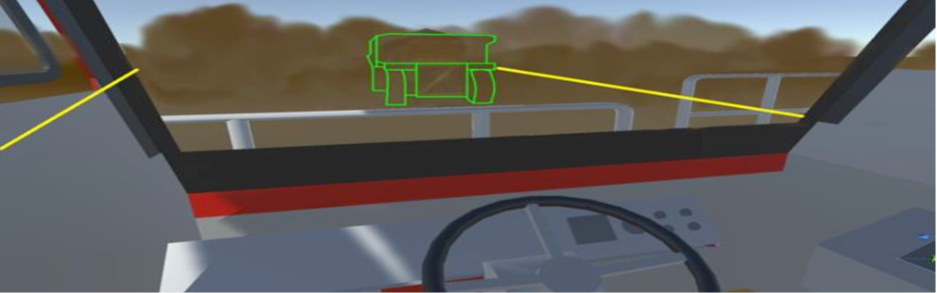
One of the most important aspects of manufacturing is ensuring workers are using the machinery as intended. Improper usage can lead to worker injuries or damage the machine. In the case of managing large or expensive to use equipment, training can become quite expensive as new employees learn how to use the machine2. In this sort of scenario, both Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) have a large potential to improve current processes. Employees can use VR to try using the machine without fear of hurting themselves or breaking the equipment. Once they have mastered the machine virtually, they can use useful tools with AR to receive visual instructions that overlay on top of the equipment, so they know exactly what to do. AR can also help experienced employees as real time data can be displayed in front of the employee and they can make decisions based on that.
Simulation Testing
As new equipment gets produced, manufactures will have to test them out in production before deploying them full scale. Here, a digital replicate of the machine can be created and using sensors a predictive analysis can be done to understand how the machine performs. This helps prevent expensive implementations of machines that may not be required. It also helps prevent downtime for new machines as the factory knows exactly how to use it when they deploy it.

Robotics impact on Labor
According to the International Federation of Robotics, 2.6 million robots are expected to be deployed by 2019, and China will account for 40% of the sale of industrial robots. The robotics market is expected to grow by 13% annually until 20193. The growth in demand for robotics clearly indicates the importance of automation in key markets like China. There is some fear that robotics result in large amounts of lost jobs, however, there is research that says that the impact will not be as large as some predict. The use of robots in factories will lead to large amounts of cost savings, which can allow for the increase of labor demand to offset the loss of jobs. This is an important issue as the use of robots and automation becomes more popular.
Conclusion
The IIoT is a large and growing sector. There is large demand for smart machines and sensors that allow manufacturers to leverage data and make trends. This will help them produce more efficiently by saving costs in areas like energy, maintenance, and training. However, with the growing trend of automation and use of robotics, there are potential ethical issues that arise as these technologies start to replace manual labor.
Sources
- https://www.cmswire.com/internet-of-things/industrial-iot-what-it-is-and-the-trends-driving-it-in-2018/
- https://shoplogix.com/blog/industrial-iot-statistics-trends/
- https://hackernoon.com/iiot-trends-to-watch-out-for-in-2017-96c498d39017